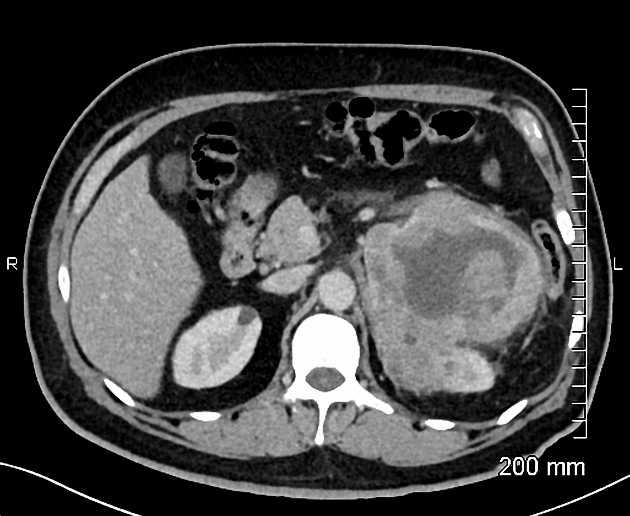
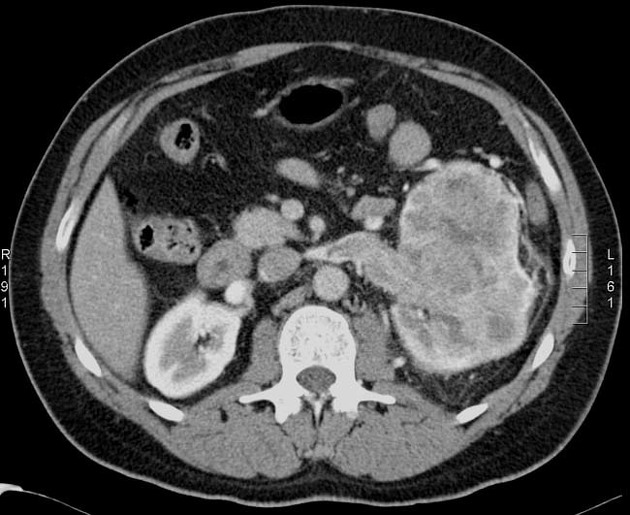
IVC lipoma








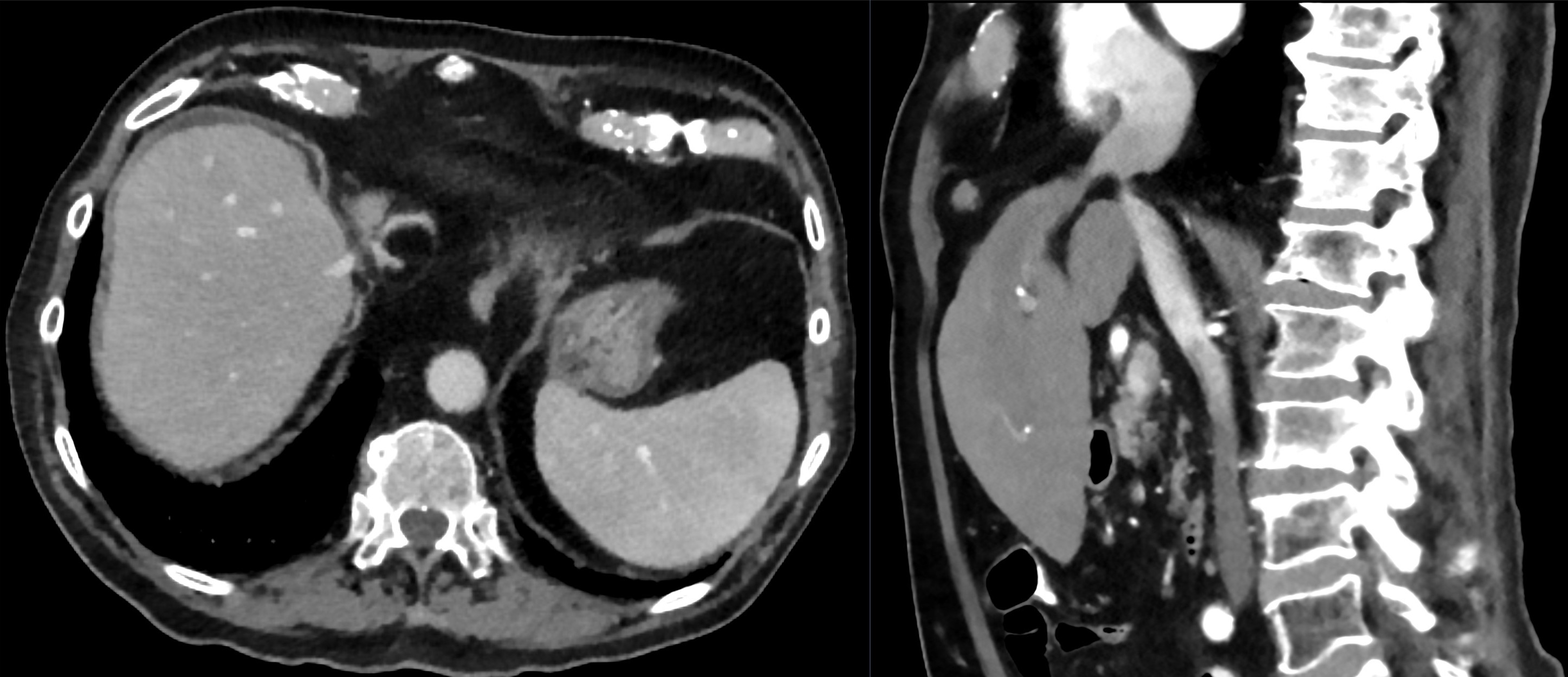


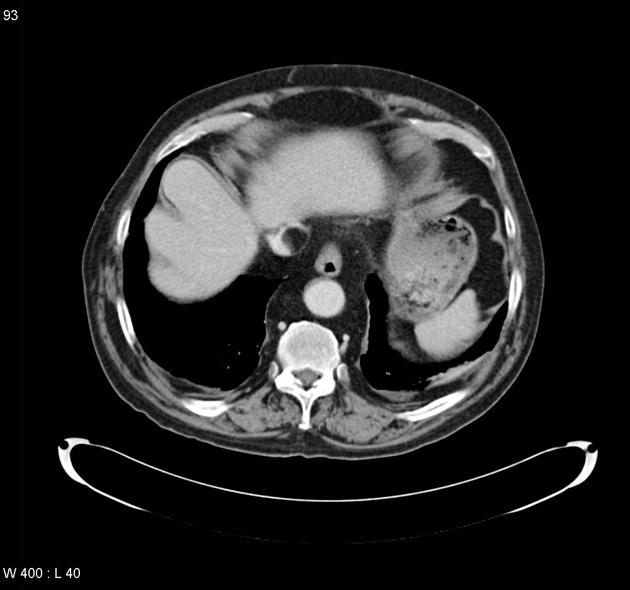
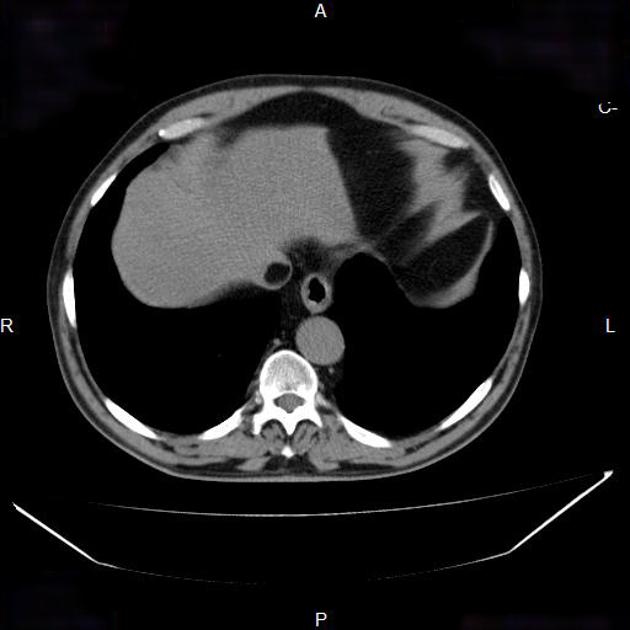
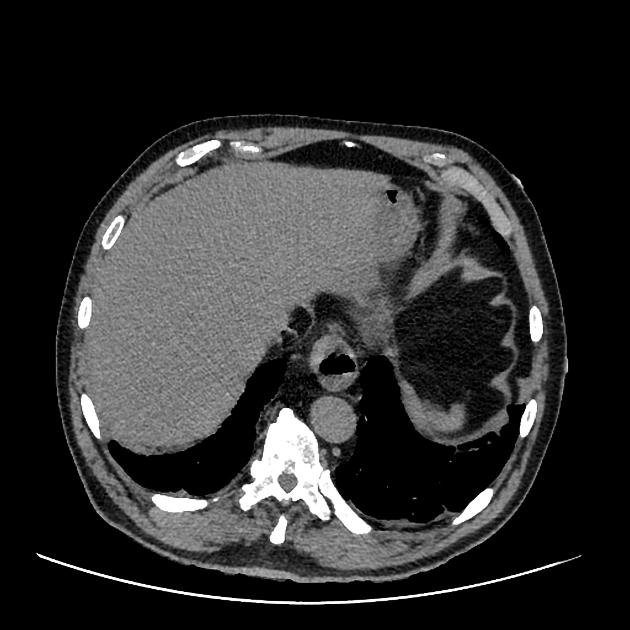
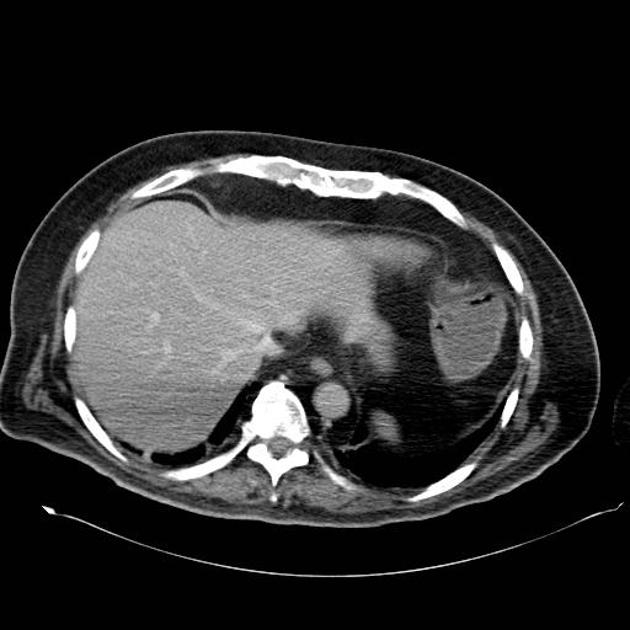
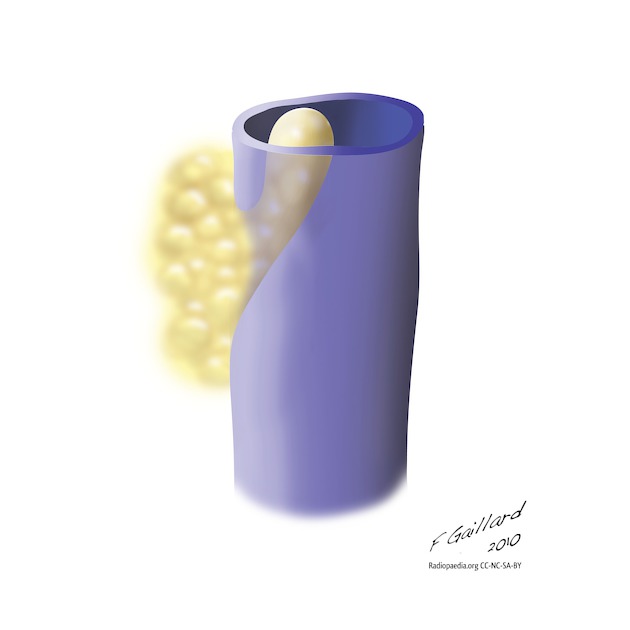
Paracaval lipoma (a.k.a. juxtacaval fat collection or pseudolipoma of the inferior vena cava) is the apparent protrusion of paracaval fat into the inferior vena cava (IVC) and is commonly visible on CT; some believe it to be a normal anatomic variant .
Epidemiology
Paracaval lipoma may be seen in up to 0.5% of CT examinations .
Associations
It may be seen in patients with cirrhosis .
Pathology
The paracaval lipoma appearance is thought to be due to volume averaging through inwards and upwards indrawing of the posteromedial wall of the inferior vena cava as a result of negative pressure created within the thorax on inspiration .
Radiographic findings
CT
Paracaval lipoma occurs at the medial aspect of the intrahepatic portion of the inferior vena cava (IVC) above the caudate lobe and represents pericaval fat appearing to invaginate into the inferior vena cava.
Differential diagnosis
On imaging consider
- bland thrombus in the inferior vena cava
- tumor thrombus
- tumors of the inferior vena cava, e.g. leiomyosarcoma
Siehe auch:
- Chiari-Netz
- Leberzirrhose
- Nierenzellkarzinom
- hepatozelluläres Karzinom
- Nebennierenrindenkarzinom
- Tumorthrombus
- Vena cava inferior Thrombose
- Kompression der Vena cava
und weiter:

 Assoziationen und Differentialdiagnosen zu lipomatöse Impression der Vena cava inferior:
Assoziationen und Differentialdiagnosen zu lipomatöse Impression der Vena cava inferior: